🚀📅 Day 29 DevOps Challenge - Jenkins Interview: CI/CD, Pipelines, Plugins, and Best Practices 🔄🛠️🧩📈🔒
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Question 1: 🤔 What’s the difference between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment?
- Question 2: 🌟 Benefits of CI/CD
- Question 3: 🧐 What is meant by CI-CD?
- Question 4: 🛠️ What is Jenkins Pipeline?
- Question 5: 🏗️ How do you configure a job in Jenkins?
- Question 6: 🐛 Where do you find errors in Jenkins?
- Question 7: 📃 In Jenkins, how can you find log files?
- Question 8: 🚀 How to create a continuous deployment in Jenkins?
- Question 9: 🚧 How to build a job in Jenkins?
- Question 10: 🌀 Why do we use a pipeline in Jenkins?
- Question 11: 🛠️ Is Only Jenkins enough for automation?
- Question 12: 🔒 How will you handle secrets in Jenkins?
- Question 13: 🔄 Explain different stages in CI-CD setup
- Question 14: 🧩 Name some of the plugins in Jenkins.
- Question 15: 🔄 Can you explain a Jenkins workflow and provide a script for this workflow?
- Endnote
Introduction
Are you ready to dive into the world of Jenkins, the powerhouse of Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)? Whether you're a seasoned DevOps engineer or just starting your journey into automation, understanding Jenkins is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore Jenkins-specific questions, delve into the intricacies of CI/CD, and uncover the best practices for DevOps automation. Let's embark on this Jenkins journey and empower ourselves with the tools and knowledge needed to excel in the world of DevOps. 🔄🛠️🌟
![Compromising CI/CD Pipelines with Leaked Credentials [Security Zines]](https://blog.gitguardian.com/content/images/2022/04/22W15-blog-SecurityZines-Compromising_CICD_pipelinesnal.jpg)
Question 1: 🤔 What’s the difference between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment?
Answer: Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of frequently integrating code changes into a shared repository, typically several times a day. Automated tests are run to detect integration issues, ensuring that new code additions don't break the existing codebase. 🔄
Continuous Delivery (CD) extends CI by automatically deploying code changes to a staging environment after they pass automated tests. However, CD requires human intervention to promote changes to the production environment, ensuring a final layer of approval and quality control. 🚚
Continuous Deployment (CD) goes a step further by fully automating the deployment process. Once code changes pass tests in the staging environment, they are automatically deployed to the production environment without the need for human intervention. This approach minimizes manual processes and accelerates the release cycle. 🚀
Question 2: 🌟 Benefits of CI/CD
Answer: The benefits of CI/CD include:
Faster Development Cycles: CI/CD automates repetitive tasks, reducing deployment time and enabling quicker feature delivery. ⏩
Reduced Manual Errors: Automation reduces the likelihood of human error during deployments. 🤖
Early Bug Detection: Continuous testing detects issues early in the development process, making them easier and cheaper to fix. 🐞
Consistent and Reliable Deployments: CD ensures that deployments are consistent across environments, reducing discrepancies. 🔄
Continuous Feedback and Improvement: Frequent deployments and automated testing provide a feedback loop for continuous improvement. 🔄📈
Enhanced Collaboration: CI/CD promotes collaboration among development, testing, and operations teams, improving communication and efficiency. 👥🤝

Question 3: 🧐 What is meant by CI-CD?
Answer: CI-CD, short for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment, is a software development and deployment approach focused on automation and collaboration. It involves continuously integrating code changes, running automated tests, and deploying code to various environments (e.g., staging and production). CI-CD ensures that software changes are delivered reliably, rapidly, and with minimal manual intervention. 🔄🚀
Question 4: 🛠️ What is Jenkins Pipeline?
Answer: Jenkins Pipeline is a suite of plugins that allows you to define and automate your build and deployment processes as code. It uses a domain-specific language based on Groovy and allows you to create a structured, versionable, and repeatable set of steps for building, testing, and deploying applications. Jenkins Pipeline makes it easier to visualize and manage complex workflows. 🧰🛠️
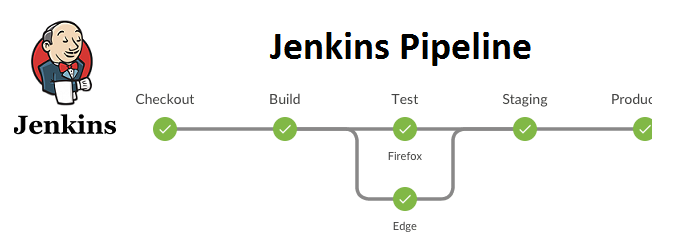
Question 5: 🏗️ How do you configure a job in Jenkins?
Answer: To configure a job in Jenkins, follow these steps:
Log In: Log in to the Jenkins web interface. 👩💻🔑
Create a New Job: Click on "New Item" or "New Job" to create a new job. 🆕
Job Configuration: Configure the job by specifying its name, type (e.g., freestyle or pipeline), and other settings. 📝
Build Steps: Define the build steps, which include tasks like compiling code, running tests, and packaging artifacts. 🏗️
Source Code Management: Configure source code management settings if your job interacts with a version control system. 📦🧑💻
Post-Build Actions: Set up post-build actions, such as archiving artifacts, sending notifications, or triggering downstream jobs. 📤📨
Save: Save the job configuration. 💾
Question 6: 🐛 Where do you find errors in Jenkins?
Answer: In Jenkins, errors can be found in several places:
Build Console Output: Errors and logs related to a specific job can be found in the "Build Console Output" of that job. This is where you'll see detailed information about the execution of the job, including error messages. 📃🐞
Jenkins System Log: System-wide errors and logs can be found in the Jenkins system log, which provides information about the entire Jenkins instance. 📋🔍
Job Configuration: Errors related to job configuration can be found in the job's configuration page if there are issues with the setup. 📝🔧
Plugin Logs: If you're using specific plugins, errors related to those plugins can be found in their respective logs. 🧩📊
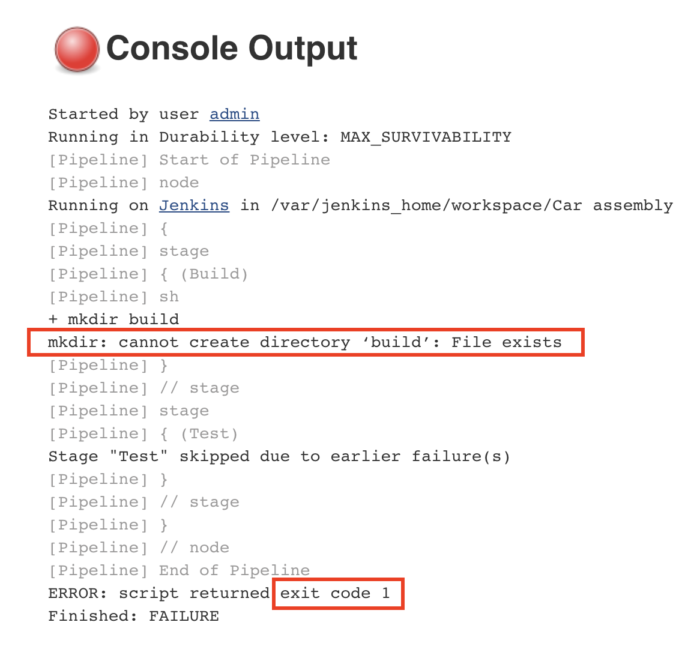
Question 7: 📃 In Jenkins, how can you find log files?
Answer: To locate log files in Jenkins:
Navigate to the specific job you're interested in. 🏃♂️
Go to the job's workspace directory, which is typically located at
JENKINS_HOME/workspace/JOB_NAME/. 📂Inside the workspace directory, you'll find log files that contain detailed information about the job's execution. 📄🔍
Question 8: 🚀 How to create a continuous deployment in Jenkins?
Answer: To set up continuous deployment in Jenkins:
Define a deployment pipeline using Jenkins Pipeline DSL or configure a freestyle job. 🛠️📦
Integrate deployment actions, such as copying artifacts to the production server or deploying Docker containers, into the pipeline. 🚢🐳
Configure the pipeline to trigger automatically after successful builds and tests. 🔄🔥
Ensure that proper access controls and approval mechanisms are in place, depending on your deployment strategy. 🔒✅
Test the pipeline thoroughly to validate the automated deployment process. 🧪📊
Question 9: 🚧 How to build a job in Jenkins?
Answer: To build a job in Jenkins:
Job Configuration: Configure a new or existing job by specifying its name and type. 📝🆕
Build Steps: Define the build steps within the job, including tasks like compiling code, running tests, and generating artifacts. 🏗️🔧
Source Code Management: Configure source code management settings if your job interacts with a version control system. 📦🧑💻
Post-Build Actions: Set up post-build actions, such as archiving artifacts, sending notifications, or triggering downstream jobs. 📤📨
Build Trigger: Configure when the job should be triggered, either manually or automatically based on changes in the repository. ⏲️🔄
Save: Save the job configuration, and you can trigger the build manually or through automation. 💾🚀
Question 10: 🌀 Why do we use a pipeline in Jenkins?
Answer: Pipelines in Jenkins are used for several reasons:
Structured Workflow: Pipelines provide a structured and visual representation of complex build and deployment workflows, making them easier to understand and manage. 📊🌐
Version Control: Pipelines as code can be stored in version control systems, ensuring that the workflow is versioned and reproducible. 📂🔄
Automation: Jenkins Pipelines automate the entire CI/CD process, reducing manual interventions and errors. 🤖🔁
Parallel Execution: Pipelines enable parallel execution of tasks, optimizing resource usage and speeding up the delivery process. ⏩🚀
Monitoring and Visualization: Pipelines offer real-time monitoring and visualization of the entire process, making it easier to identify bottlenecks and issues. 📈👀
Question 11: 🛠️ Is Only Jenkins enough for automation?
Answer: While Jenkins is a powerful automation tool, its scope is primarily focused on CI/CD and build automation. Depending on your automation needs, you may require additional tools for configuration management (e.g., Ansible or Puppet), container orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes), infrastructure provisioning (e.g., Terraform), and monitoring (e.g., Prometheus). The choice of tools depends on the specific requirements of your automation tasks. 🧰🤖
Question 12: 🔒 How will you handle secrets in Jenkins?
Answer: Handling secrets in Jenkins involves using plugins like "Credentials Binding" or "Secrets Management." These plugins provide secure storage and usage of sensitive information, such as API keys or passwords. Secrets are encrypted and can be accessed within your Jenkins jobs or pipelines securely. 🔑🔒

Question 13: 🔄 Explain different stages in CI-CD setup
Answer: In a CI-CD setup, different stages represent the steps involved in delivering software from development to production. These stages ensure a systematic and automated approach to software delivery. Here are the typical stages in a CI-CD setup:
Source Control: This is where code changes are managed and versioned using tools like Git. Developers collaborate by committing code to a shared repository.
Build: In this stage, code is compiled, dependencies are resolved, and artifacts are created. It ensures that the software can be built successfully.
Test: Automated tests, including unit tests, integration tests, and functional tests, are run to validate the quality of the code. Any issues detected here are addressed before proceeding.
Deploy to Staging: Code changes that pass tests are deployed to a staging environment that closely resembles the production environment. This allows for final testing and validation in a controlled environment.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): In this stage, end-users or QA teams test the software in a staging environment to ensure it meets business requirements. Any user-reported issues are addressed.
Deploy to Production: Once UAT is successful and all checks are passed, the code changes are automatically or manually deployed to the production environment, making them accessible to end-users.
Monitoring and Feedback: Continuous monitoring of the production environment provides real-time feedback on performance, errors, and user behavior. This data is used to further refine and improve the software.
![Building a CI/CD pipeline [Guide] - RevDeBug](https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/4447326/Diagram_2.png)
Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring that code changes are thoroughly tested and validated before reaching production, resulting in a reliable and efficient software delivery process. 🔄🚀🧪🌐
Question 14: 🧩 Name some of the plugins in Jenkins.
Answer: Jenkins has a vast ecosystem of plugins that enhance its functionality and integrate with various tools and technologies. Some popular Jenkins plugins include:
Git Plugin: Integrates Jenkins with Git repositories for source code management.
Docker Plugin: Facilitates the management and deployment of Docker containers within Jenkins jobs.
JUnit Plugin: Publishes JUnit test results and provides reporting on test outcomes.
Pipeline Plugin: Enables the creation and management of Jenkins Pipeline jobs for defining complex build and deployment workflows.
Credentials Binding Plugin: Helps manage and secure sensitive information, such as API keys and credentials, used within Jenkins jobs.
Email Extension Plugin: Allows the sending of customizable email notifications based on build and job statuses.
Ansible Plugin: Integrates Jenkins with Ansible, a popular configuration management and automation tool.
Prometheus Plugin: Enables monitoring and metrics collection within Jenkins, compatible with the Prometheus monitoring system.
Kubernetes Plugin: Facilitates interaction with Kubernetes clusters for container orchestration.
SonarQube Scanner Plugin: Integrates Jenkins with SonarQube for static code analysis and code quality checks.

These plugins extend Jenkins' capabilities and make it adaptable to a wide range of use cases, from source code management to automated testing, deployment, and monitoring. 🧩🔌🤖
Question 15: 🔄 Can you explain a Jenkins workflow and provide a script for this workflow?
Answer: Certainly! A Jenkins workflow involves defining a series of stages and actions to automate your Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) process. You can use the Jenkins Pipeline DSL (Domain-Specific Language) to create and manage these workflows. Below is an example of a Jenkins Pipeline script for a basic CI/CD workflow:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Checkout') {
steps {
// Checkout your source code from a Git repository
checkout scm
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
// Compile and build your project (replace with your build tool)
sh 'mvn clean package'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
// Run automated tests (replace with your testing framework)
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
stage('Deploy to Staging') {
steps {
// Deploy to a staging environment (replace with your deployment process)
sh 'ansible-playbook deploy-staging.yml'
}
}
stage('User Acceptance Testing (UAT)') {
steps {
// Perform user acceptance tests in the staging environment
sh 'robot uat_tests.robot'
}
}
stage('Deploy to Production') {
when {
// Define conditions for deploying to production (e.g., manual approval)
expression { currentBuild.resultIsBetterOrEqualTo('SUCCESS') }
}
steps {
// Deploy to the production environment (replace with your deployment process)
sh 'ansible-playbook deploy-production.yml'
}
}
stage('Post-Deployment Cleanup') {
steps {
// Perform any post-deployment cleanup or notifications
sh 'echo "Deployment to production is complete."'
}
}
}
post {
success {
// Define actions to be taken on successful completion of all stages
echo 'CI/CD Pipeline completed successfully!'
}
failure {
// Define actions to be taken on pipeline failure
echo 'CI/CD Pipeline failed. Please investigate.'
}
}
}
This Jenkins Pipeline script represents a basic CI/CD workflow with various stages, including source code checkout, building, testing, deploying to staging and production, and performing post-deployment tasks. It also includes a post section to define actions based on the pipeline's success or failure.
Please note that this is a simplified example, and you should adapt the script to your specific project's requirements, tools, and deployment processes. Jenkins Pipeline offers flexibility for customizing CI/CD workflows to suit your needs. 🔄🚀🛠️
Endnote
👏 Jenkins, the ultimate DevOps ally! With CI/CD wisdom and Jenkins' automation magic, you're well-equipped for DevOps success. Keep building, testing, and deploying with confidence. 🛠️🚀💡 #JenkinsMastery
